Knowledge Software In The Contact Centre
As the beating heart of so many clients’ customer service operations and with expectations constantly evolving, contact centres and BPOs are feeling the pressure to promote efficiency and maintain CSAT – all while keeping costs down.
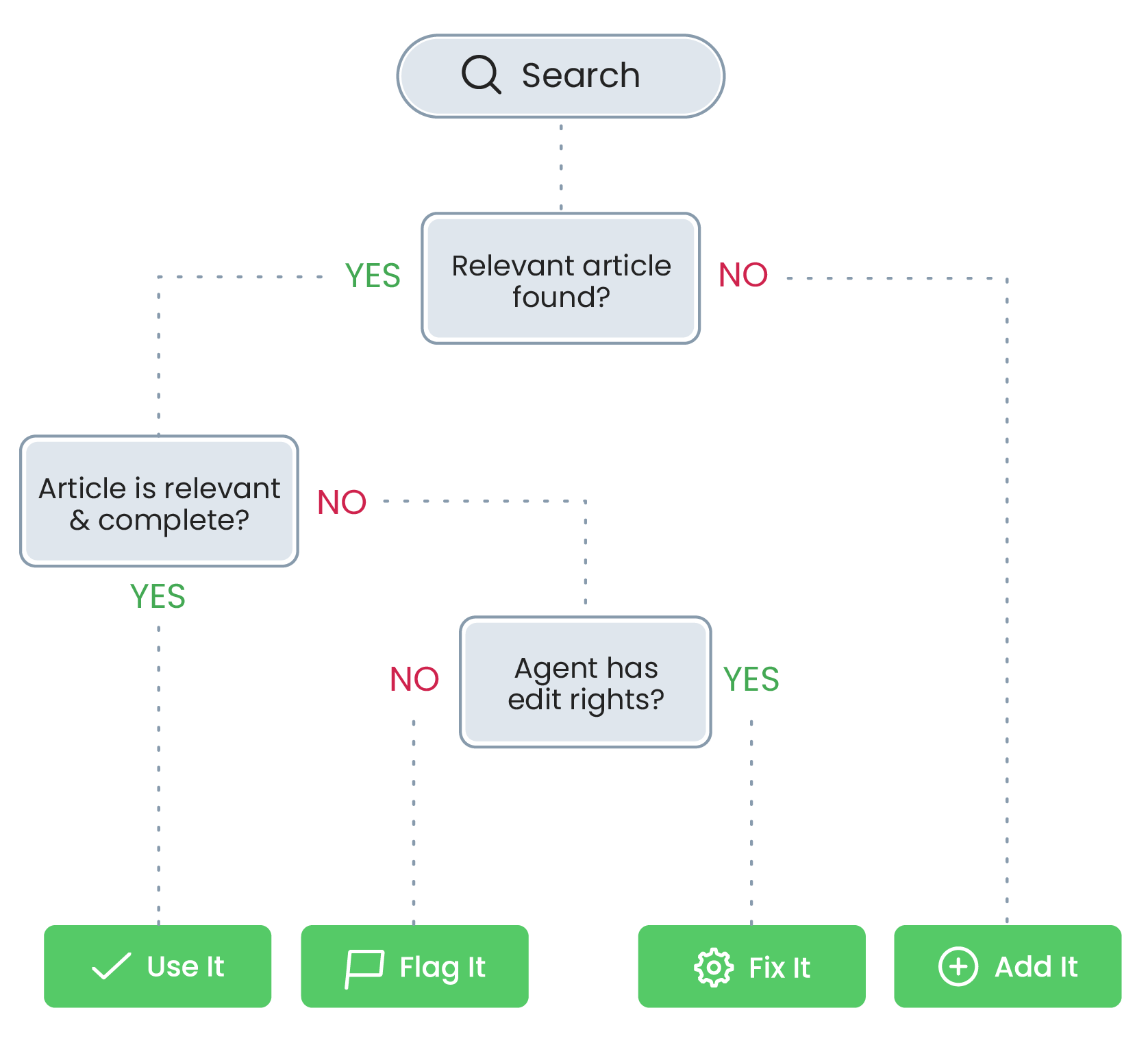
So, how does knowledge software: an agent knowledge base interface (internal-facing) and web self-service tools (public-facing) help improve contact centre efficiency, customer experience and satisfaction? Here we explore this topic in detail.
The Central Source Of Truth
A knowledge base plays a key role within not only the contact centre but the overall business. It acts as a centralised library of knowledge, your company’s single source of information; everything from HR policies, suitable for internal eyes only, to step-by-step tutorials that can be easily found and digested by your site visitors.
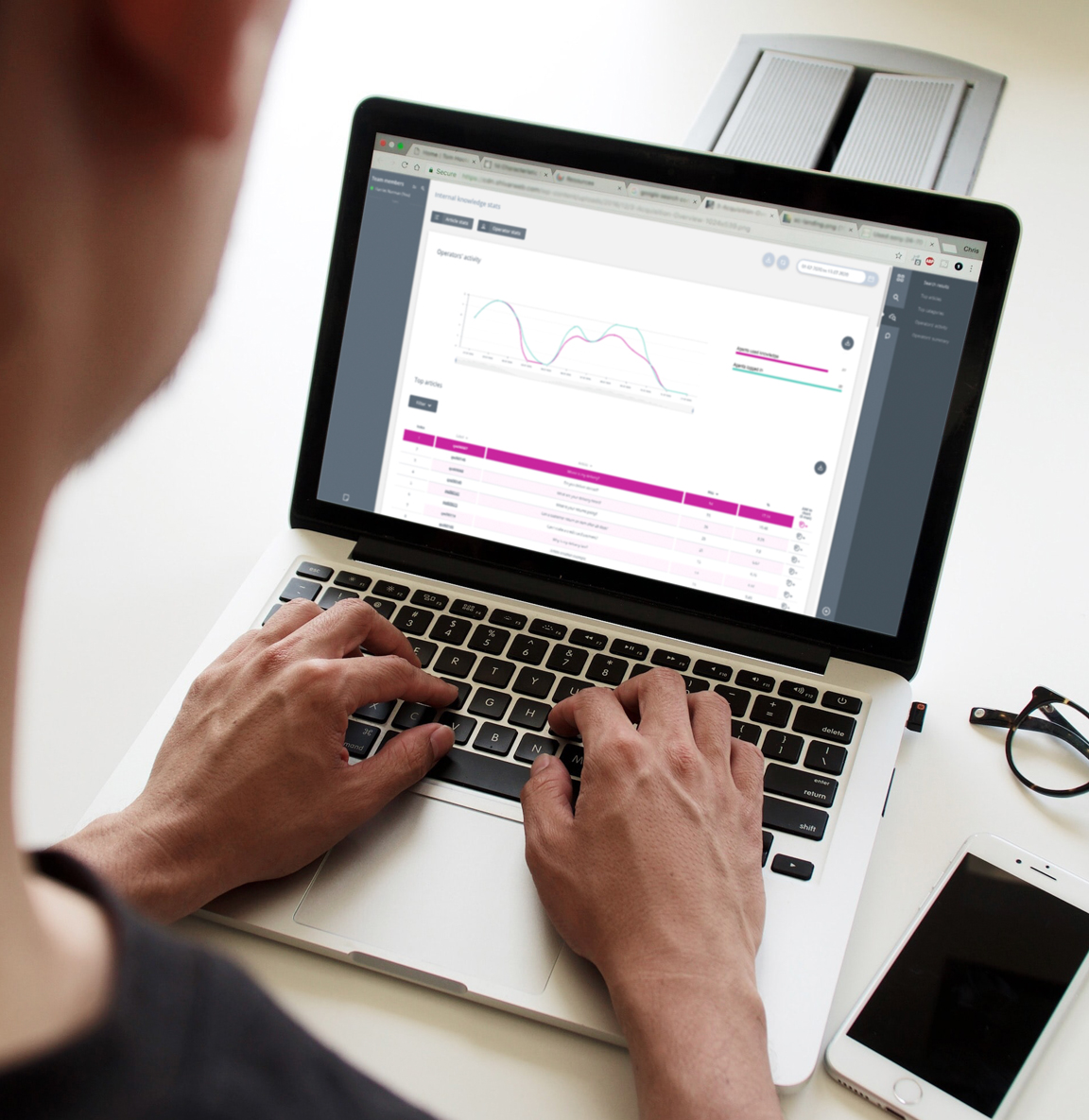
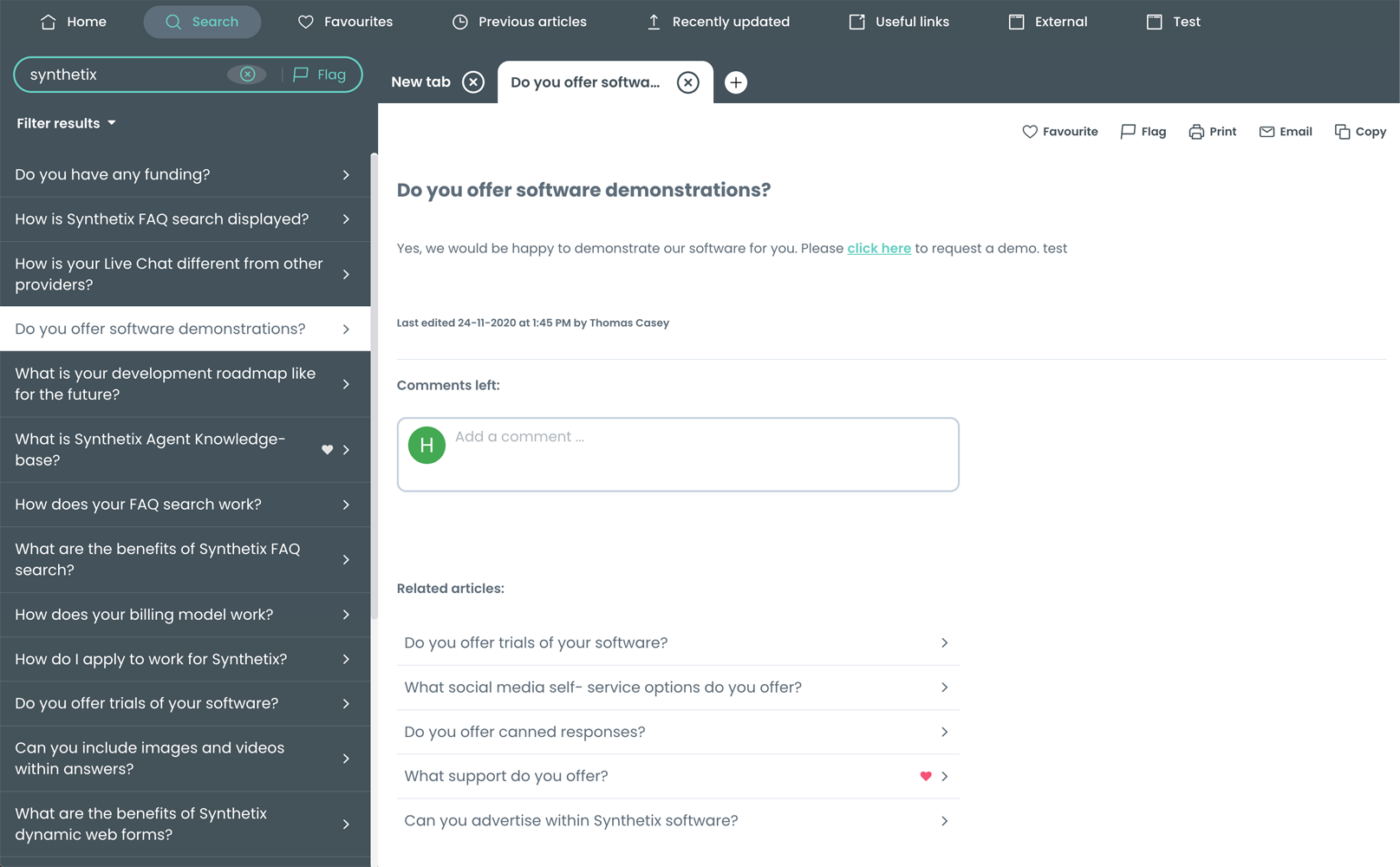
Synthetix’s knowledge base, for instance, resides at the centre of your clients’ customer service operations. It contains knowledge articles that are essentially the answers to popular queries. These can be categorised and assigned to views, for example, clients usually have both internal and public views, each of which containing very different content suitable to their appropriate audience.
Powered by AI, our intelligent knowledge base utilises sophisticated Natural Language Processing (NLP) which gets to work when a user begins typing a query into the search bar. NLP picks apart the query, analysing each component including keywords, grammar, intent and popularity to return the most relevant articles.
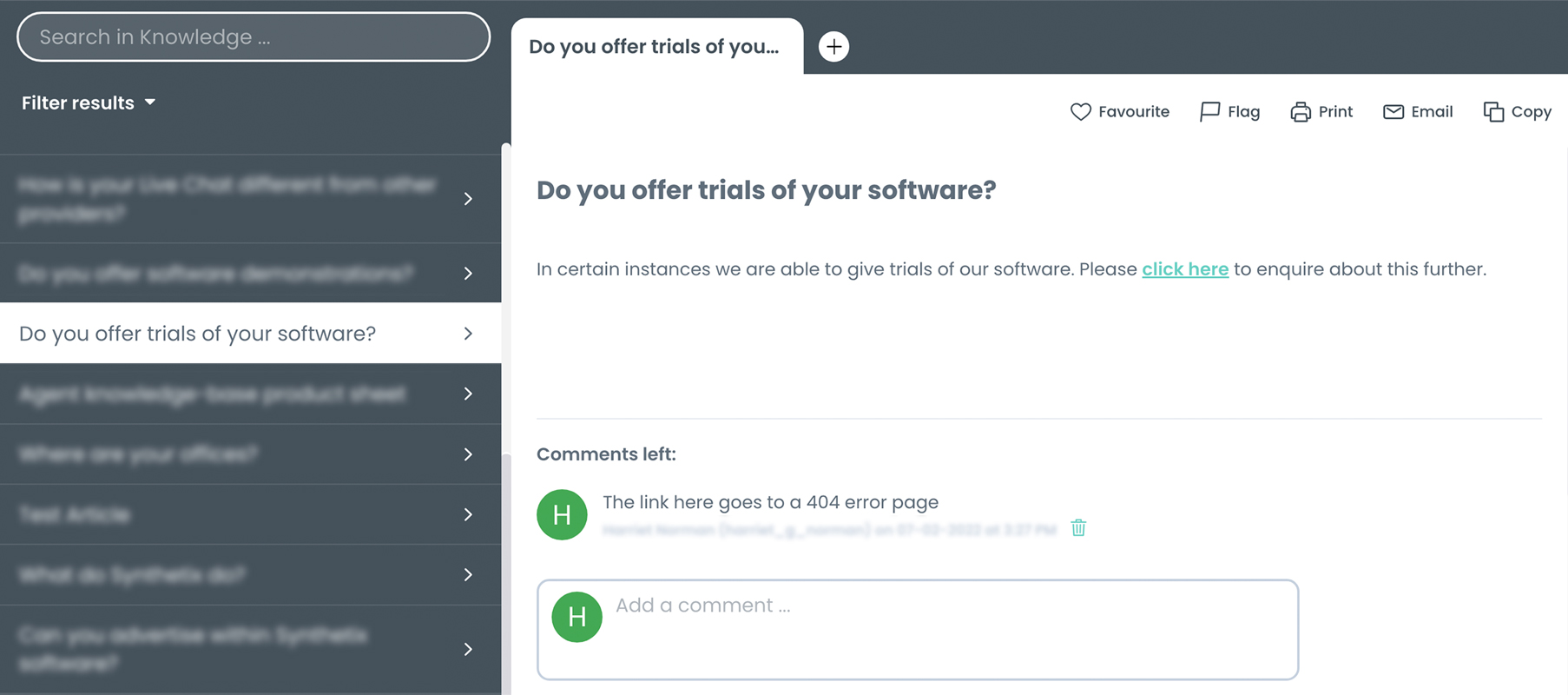
The knowledge base provides fundamental information internally to employees but also agents in the contact centre who are helping customers over the phone or live chat. It also provides information externally. The knowledge base fuels self-service channels so that customers can answer their own questions when on your website.
Knowledge Software And Your Agents
Knowledge software is your agents’ most powerful tool in the contact centre. Whether they access it whilst on the phone or live chat with a customer, It equips your agents with the information necessary to resolve customer queries in the most efficient manner. With a library of knowledge available at their fingertips, contact centre efficiency and support costs dramatically improve.
Average Handling Time (AHT) Reduction
With quick access to knowledge articles, agents no longer have to search through resources or intranets using multiple windows, hoping that the answer they have found matches the question that has been asked.
Synthetix’s agent knowledge base, Knowledge: For Your Team not only utilises NLP to provide quick solutions and therefore reduces Average Handling Times (AHT) but for further efficiency, the AI-predictive suggestions function.
AI-predictive suggestions harness powerful NLP and recommend relevant knowledge articles to the agent based on what keywords are being entered. These suggestions are updated on each key-press, all the agent must do is click to copy and the resolution is provided.
Live chat agents can optimise handling times even further using our live key-press feed feature. It allows the agent to preview what a customer is typing in real-time before they hit “send”. This lets them problem-solve and prepare a resolution as the query is sent, reducing AHT and improving CX.
First Contact Resolution (FCR) Improvement
First Contact Resolution (FCR), the rate at which a customer query is resolved on the first call or contact with a contact centre agent is fundamental to customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Poor FCR happens all too often and can stem from a number of things, leaving customers feeling frustrated and dissatisfied. When a customer has to call back in because the answer they were initially given is incorrect it is generally down to the knowledge base.
When inconsistent or inaccurate information is provided to a customer, it is usually because a company’s information sources have not been updated. For instance, a policy change occurs but only the website FAQs are updated, leaving the internal knowledge base with old, inaccurate details.
A centralised knowledge base, on the other hand, controls all sources of information and reflects and updates in real-time.
Agent Satisfaction
As NLP takes effect in customer self-service channels such as FAQ tools and chatbots, the volume of routine queries that ultimately reach the contact centre are significantly reduced. Instead of agents dealing with the same, common queries, AI instead handles them.
This removes the mundane from agents’ jobs and allows them the bandwidth required to deal with customer queries that are complex by nature and require human understanding and reasoning. Helping people through their problems gives employees a sense of purpose and therefore increases job satisfaction and enrichment.
Furthermore, when provided with software that is easy to use and genuinely helpful, the working day becomes more enjoyable and efficient, for example:
- An integrated knowledge base that resides within the agent’s internal interface.
- AI-predictive suggestions that recommend articles based on what an agent is typing in.
- NLP-fuelled technology that ensures the relevancy and consistency of answers.
- A “Favourites” function for quick access to commonly used articles, avoiding the need for repetitive searching.
Training Optimisation
With an AI-powered knowledge base acting as the ultimate training tool, providing new starters with a library full of knowledge, training times can be reduced on average by 30%
Answers that are available at a keypress significantly reduces the time in which it would otherwise take to onboard and train a new agent.
Synthetix’s internal knowledge base solution, Knowledge: For Your Team includes agent scripting, powered by simple decision tree technology. Transform your newest employees into seasoned experts by providing them with multi-step decision trees to follow, helping them complete processes and problem-solving with ease.
Knowledge Software And Customers
Intelligent knowledge base software powers a range of external-facing channels that aim to help customers find answers to their own questions.
The centralised knowledge base powers customer self-service channels such as chatbots, FAQ tools and SEO help centres. This ensures that the information in which agents are serving customers via live chat and telephone is the same that customers are served via web self-service tools.
Knowledge software not only provides site visitors with the tools to find the answers to their own resolutions efficiently, but it also boosts CSAT ratings whilst contributing to significant support cost reductions.
Contact Centre Cost Reductions
Synthetix’s AI-powered self-service tools utilise sophisticated NLP to automate routine queries and tasks online, deflecting the volume of contact that would otherwise reach the contact centre. This in turn helps to reduce the accumulation of costs associated with handling a query, bringing overall support costs down.
Further, fewer routine queries reaching the contact centre means that, for those that have complex issues and require the help of contact centre agents, wait time is significantly less which contributes to CSAT.
Customer Satisfaction
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) increases the likeliness that the right answer will be served at an efficient rate thanks to its mechanisms.
- The option to self-serve. In one survey, 67% of respondents said they would rather self-serve than talk to a company representative. Customers want the freedom to find their own resolution where possible.
- Self-service channels contribute to and maintain CX. The automation of routine queries online means that those who need to contact the contact centre experience a smaller wait time and greater bandwidth from agents now that they are less congested with routine questions.
- Customers can find the answers to their questions 24/7/365. AI does not need to take breaks or holidays and therefore can help serve customers at any time. This is particularly important for example if customers need emergency information during the early hours of the morning when the contact centre is not open.
Smooth Customer Journeys
SEO Help Centre
Chatbots
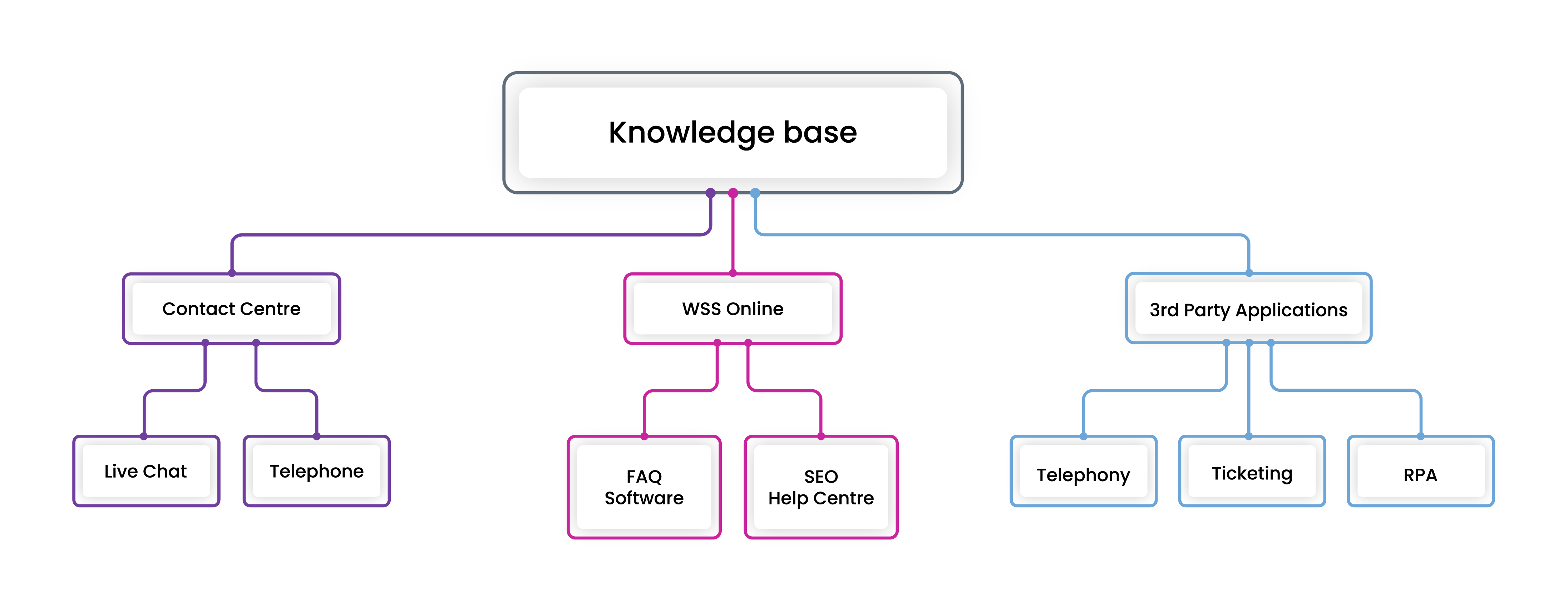
Knowledge Software And Your Software
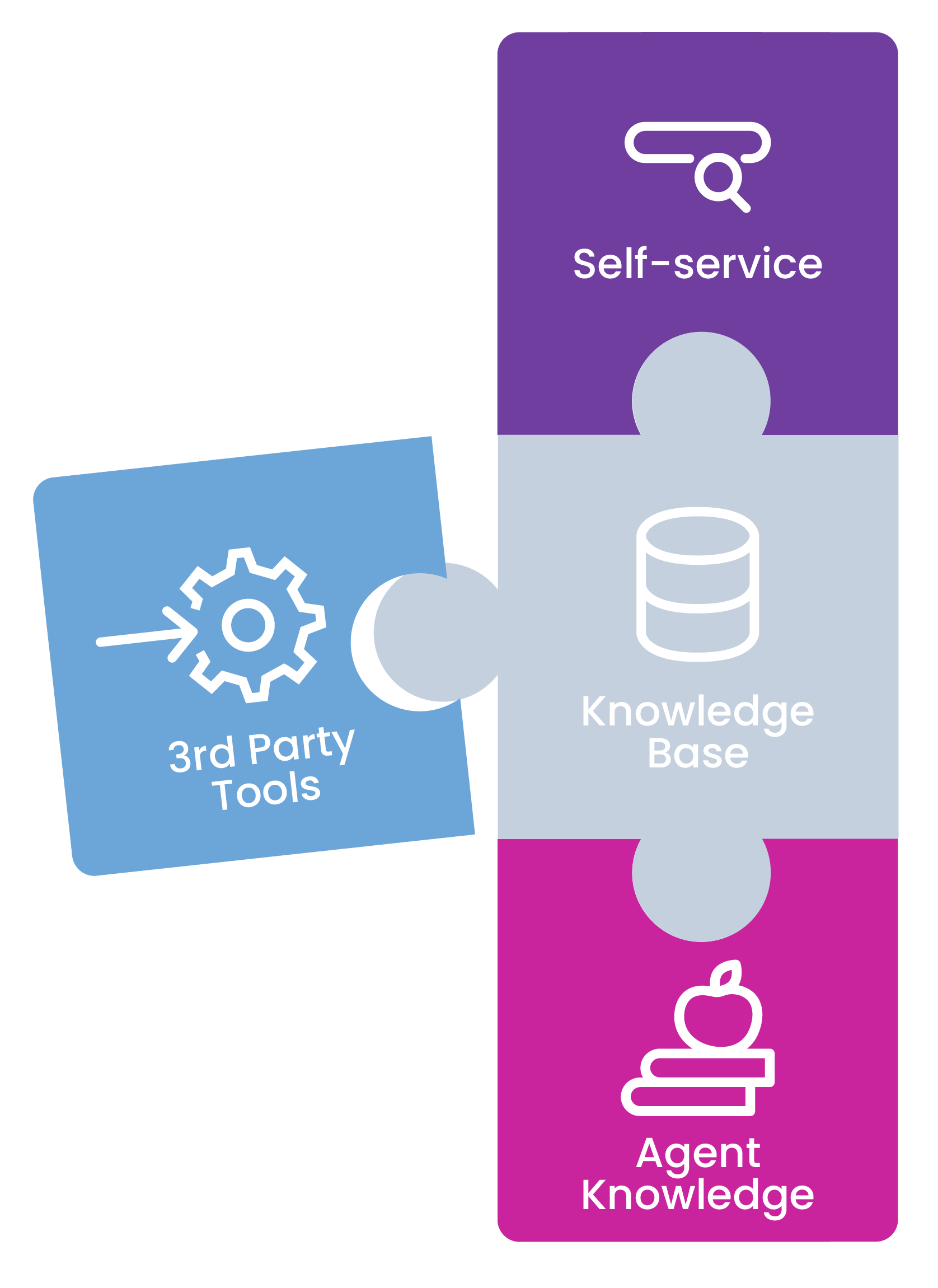
When you connect knowledge software – both agent-facing and customer-facing – with your everyday business tools, capabilities are unlocked, operational efficiency is boosted and you can better serve your clients’ customers.
When it comes to integrating knowledge software with the 3rd party applications you rely on daily, the whole is greater than the sum of its parts.
Ticketing
Telephony
By connecting knowledge base software with telephony tools, contact centre agents are equipped with quick access to answers, powered by NLP and within the same interface. This helps improve agent efficiency, improve CX, reduce Average Handling Times (AHT) and therefore support costs.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Develop your existing RPAs further by integrating with knowledge software, whether that’s internal knowledge base software or web self-service tools.
Expand current automation to generate a more valuable, efficient outcome. With capabilities to share critical 2-way data across platforms, companies benefit from significant operational efficiency, cost savings and enhanced CX.