Chatbots: Taking CX By Storm
Just decades ago, chatbots were considered futuristic or gadget-like, they were innovations with a huge untapped potential for CX. The chatbots we are familiar with today, however, are functional customer service tools that have taken CX by storm, particularly in recent years.
For many businesses, chatbot are now deemed essential – if they aren’t already part of the existing technology stack, they are quickly making their way onto CX roadmaps across industries. According to one study, 77% of executives have already implemented and 60% plan to implement chatbots for after-sales and customer service.
For customers, chatbots provide familiarity, convenience and instant access to relevant information on your company, products or services. This not only enhances CX but drives demand as the global chatbot market is expected to grow from $2.6 billion in 2019 to $9.4 billion by 2024 at a CAGR of 29.7%. For companies who wish to remain competitive but are yet to implement chatbots into their current offering, they are worth considering.
Simple Vs Conversational Chatbots
There are major differences between simple and conversational chatbots that can affect your customers considerably. Whilst simple chatbots often seem the more cost-effective option, when it comes to fulfilling your long-term CX strategy, this is where they fall short.
Types of Chatbot
There are 3 common chatbot types used in customer service, these include:
- Menu-based chatbots
- Keyword recognition chatbots
- Conversational chatbots
Menu-based
chatbots
Keyword recognition
chatbots
Conversational
chatbots
Menu-Based Chatbots
Using menu buttons to help customers navigate to the answer required, this chatbot type has basic functionality. Menu-based chatbots are built on rule-based automation as opposed to AI, which means that they can only respond to queries that match their pre-loaded responses exactly. The limitation here is this chatbot will not recognise even the smallest query variation, this results in a dead-end response without the capability to further attempt to understand what a customer is asking.
Whilst this simple chatbot type might be adequate for very small or start-up businesses with extremely basic needs, for example serving a fixed set of FAQs, it is not sustainable for larger companies with more sophisticated CX goals.
Keyword Recognition Chatbots
This type of chatbot utilises basic AI to break down the query at hand, analysing each keyword to deliver the most relevant result. By focusing on different word classes, keyword recognition chatbots can determine the most suitable response. For instance, by isolating keywords “renew” and “subscription” or “setup” and “account”, the chatbot can assume the customer’s requirement and send a response based on this.
Although keyword-recognition chatbots harness AI to some extent, they are not effective at recognising and conversing with multiple query variations.
Conversational Chatbots
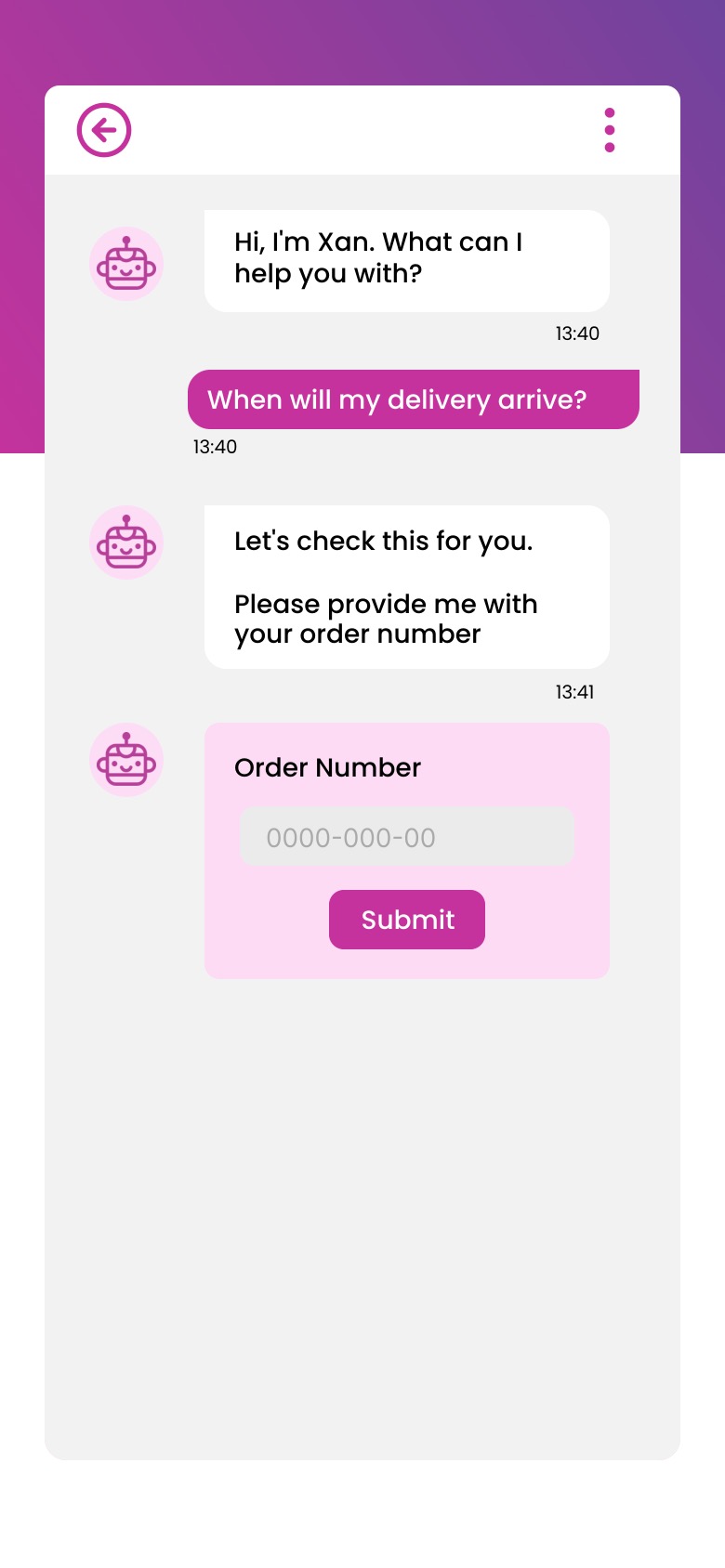
When it comes to delivering CX, conversational chatbots are by far the most effective type of chatbot. These advanced tools utilise AI, harnessing Natural Language Processing (NLP) to understand the context and intent of the question that is asked. This means that multiple variations of the same query can be asked and an identical answer is delivered seamlessly. Even if a question is not immediately obvious, conversational chatbots use decision tree technology to ask a series of questions until a resolution is found.
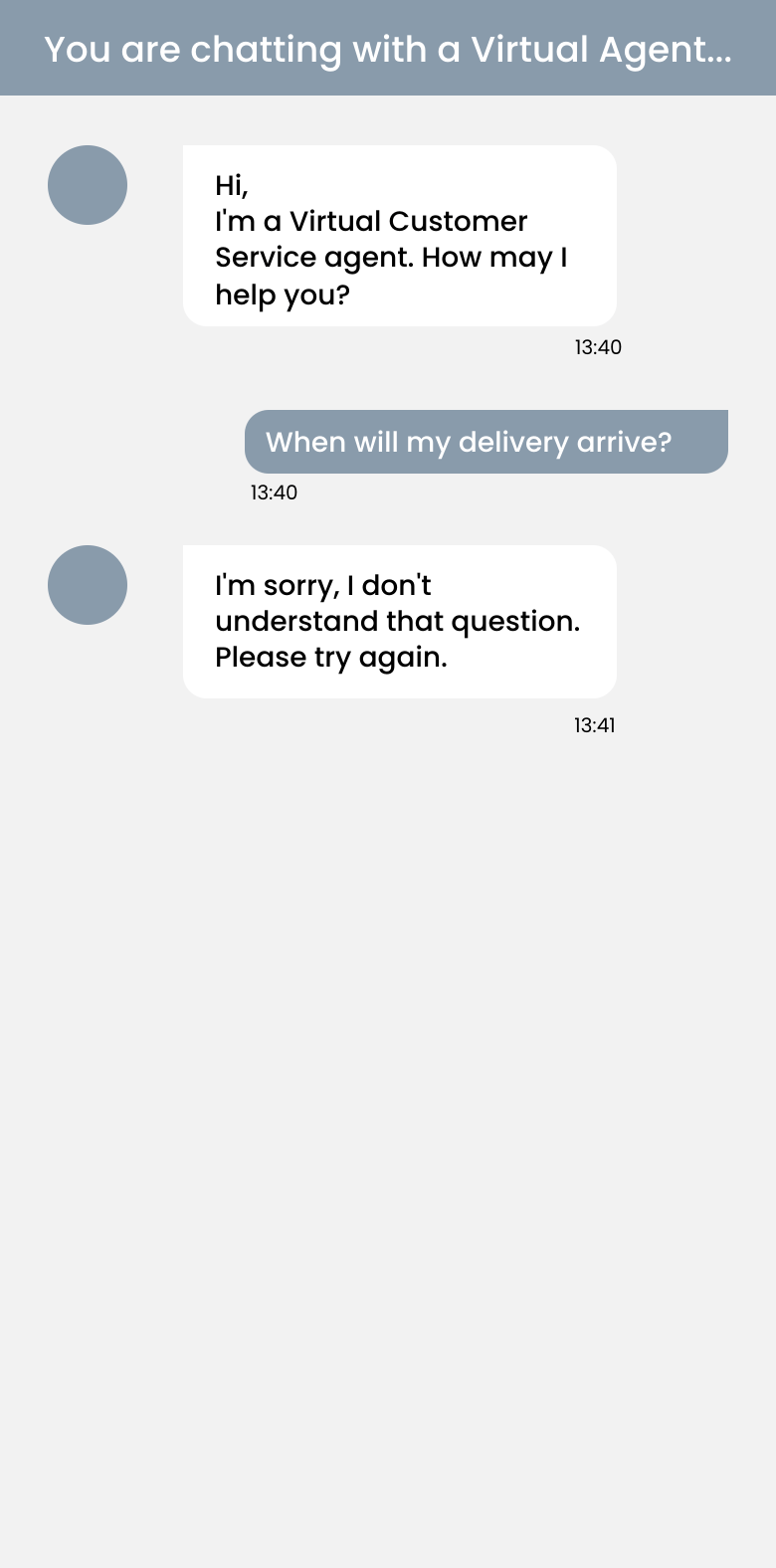
Conversational chatbots will never serve the response: “I’m sorry I don’t understand the question. Please try again.”
Unlike its basic alternatives, this chatbot type can be configured to naturally converse with customers, adding character to the experience whilst conveying brand personality. Through machine learning principles the CX is further enhanced as customer journeys are personalised; conversational chatbots can learn, store and use customer information for future sessions. By remembering certain details and preferences CX is of optimal efficacy.
Basic, rule-based chatbot
AI-powered chatbot
Why Conversational Chatbots?
A report by Gartner reveals that 91% of organisations plan to deploy AI by 2022. Another report suggests that by 2025, 80% of large enterprises will need to have a “conversational-technology-focused-centre” implemented.
AI and the tools in which it powers are rightly viewed as game-changing technologies.
While AI has been around since the 1950s when Turing developed the Turing Test, followed by the debut ‘chatterbot’, ELIZA, that was developed in the 1960s, why is it that the conversational chatbots of today are experiencing such rapid adoption?
The answer is completely customer-centric; conversational chatbot adoption is customer-driven. As more and more businesses compete for customers, more and more new and innovative technologies are used to drive a high level of service. As they become accustomed to this, customers expect more from businesses in general. They want less effort and a better experience. They want the ease and convenience of using an online contact channel and the depth and personality associated with agent-assisted channels.
Chatbots do not only provide a familiar instant messaging interface for customers, contributing to an enjoyable experience, but they assist in guiding customers through their journey, from start to finish. When configured correctly, chatbots are your customer’s first port of call when looking for advice, they can be guided to their destination in a number of ways:
- Most commonly, conversational chatbots solve customers’ routine questions instantly using AI-powered automation
- For instances when customers don’t yet know the resolution they require, but know there is a problem, conversational chatbot utilise decision tree technology to take care of the problem-solving process until the correct resolution is found
- Chatbots detect when a query is non-routine and therefore escalates the customer to an agent-assisted channel such as live chat where the adequate help can be provided – all of which takes place in the same window
Conversational chatbots are not only a hit with customers but with customer service and contact centre teams alike. Their capability to automatically handle significant contact volumes allows agents to focus on the queries that are complicated by nature, boosting CSAT and agent satisfaction. As a Result, Average Handling Times (AHT) are reduced by 25% and First Contact Resolution (FCR) is increased by 80% (Synthetix research).
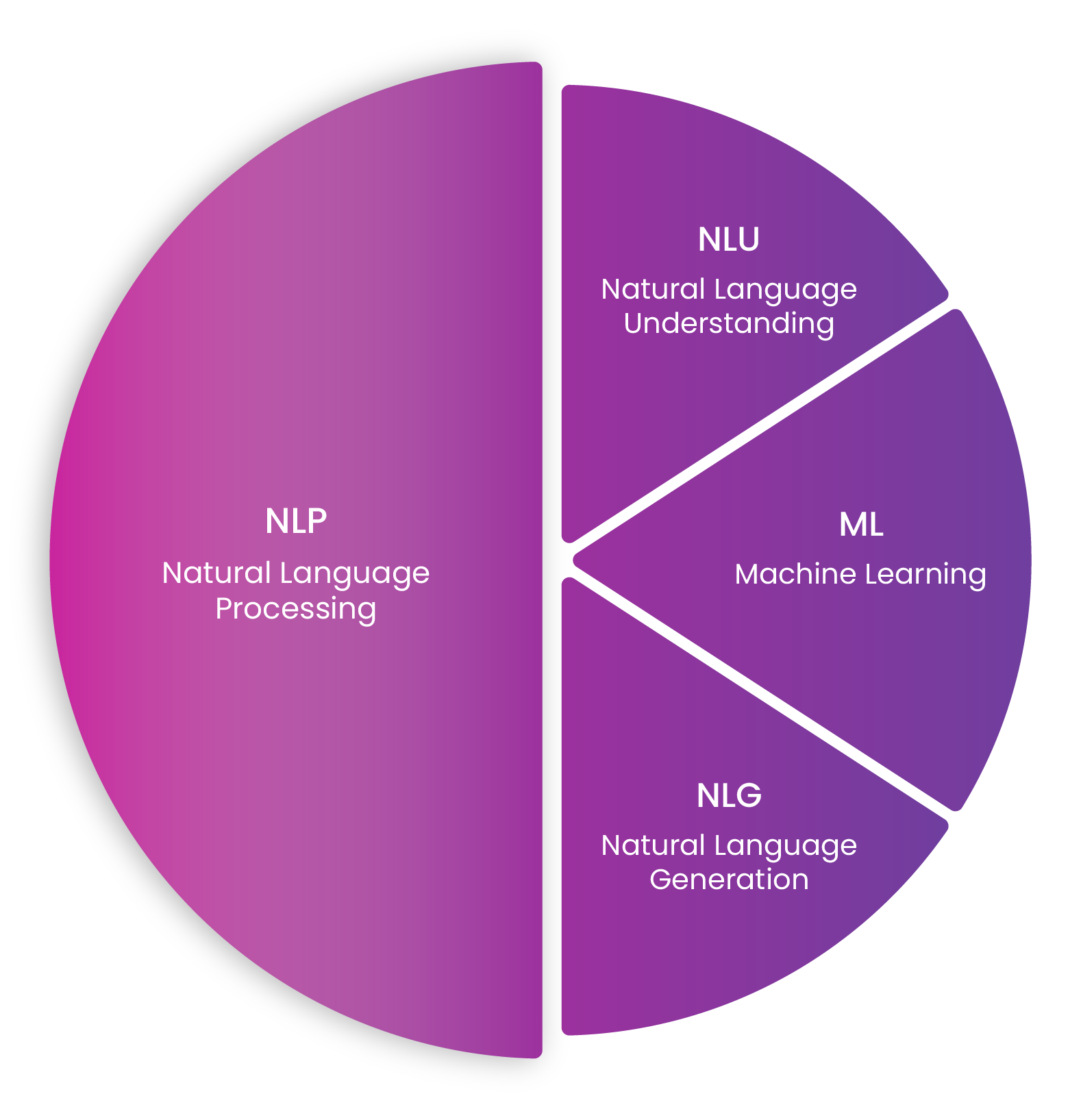
NLP, NLU, NLG & Machine Learning
How do these products of AI impact conversational chatbots and CX?
Natural Language Processing
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a branch of AI that deals with linguistics, its main purpose is to help machines understand the human language. NLP comprises Natural Language Understanding (NLU) and Natural Language Generation (NLG) to naturally interact with customers, simulating a real conversation.
Natural Language Understanding
Natural Language Understanding (NLU) uses algorithms to isolate and analyse the contents of a customer query. By identifying word classes and detecting sentiment, topics, entities and intent, NLU is essentially capable of comprehending context and what a customer is asking.
Natural Language Generation
Natural Language Generation (NLG) is the process of taking the structured data that has been produced as a result of NLU and transforming it into consumable, natural language. Algorithms that understand the construct of a naturally phrased sentence build responses based on the understanding and processing of the interaction.
Machine Learning
Machine Learning, a subset of AI surrounds the idea that computers can automatically learn and improve based on experience opposed to human intervention. Conversational chatbots adopt Machine Learning principles to personalise and enhance CX. By identifying trends in customer information, storing it and them remembering it for future interactions, chatbots create a positive and efficient experience for customers.
Implementing Conversational Chatbots
How do these products of AI impact conversational chatbots and CX?
At first glance, the implementation of conversational chatbots might seem daunting, but with the correct tools, processes and support, it’s straightforward.
Following the vendor selection process and agreed SRS, your first step depends on whether you have an existing knowledge base or not. You will either:
A. Integrate seamlessly with the chatbot so that knowledge can be shared back and forth between the knowledge database and chatbot interface
B. Collect all existing and extract any new company knowledge in order to populate your centralised knowledge base – you can find out more about the knowledge collection process here

Next, configure any secondary search layers that are responsible for understanding grammar and synonyms. For example, Synthetix’s system, “Jabberwocky” unravels customer query sentence structure to understand the meaning of any synonyms or quirks that your knowledge base is not familiar with. This ensures a conversational response is always delivered and increases accuracy. You can also configure this system to match your brand’s tone of voice so that personality is effectively conveyed during conversations.
Following successful implementation, it is good practice to closely monitor analytics for usage and trigger management data that can determine how effectively the conversational chatbot is working. Settings can be adapted and crucial decisions can be made based on such analytics for future CX improvements.
If you enjoyed this article and would like to know more about chatbots, check out our guide here. If you’d like any advice on conversational chatbots or help with implementation, please


