What Is Knowledge Management?
Knowledge management is a key business discipline that is utilised by a multitude of businesses to optimise knowledge, transforming the way it is perceived and dealt with. When executed effectively, knowledge management alters company culture so that it is centred around knowledge. Businesses that achieve this share the understanding that knowledge is a powerful asset which is everywhere and should be harnessed should they wish for growth, efficiency and improvement.
Operationally, knowledge management involves the harvesting, analysis, conversion, organisation and sharing of knowledge with the relevant audiences. This could be:
Internally for employees to use as a central library of information
Externally for customers to access knowledge through self-service tools
In contact centres for agents to use when helping customers
By embedding knowledge sharing into the company culture, the capture and collection of knowledge becomes an everyday practice for employees. This helps to remove knowledge silos within your business, promoting transparency and collaboration.
Companies that execute a successful knowledge management strategy also benefit from:
- Operational efficiency
- Agent productivity
- Reduced support costs
- Empowered employees
- Better decision making
- Improved CSAT / NPS ratings
- Growth and innovation
Knowledge Management Objectives
Like with any new initiative, your knowledge management goals and objectives must be carefully considered and finalised before anything else.
Without knowing why you are implementing knowledge management or what you aim to achieve through its impact and having everyone on the same page, the execution is likely to fail. With a clear view of the purpose and desired outcome, you ensure that everyone has the same vision and is working towards a common result. It also helps everyone involved measure their progress and question if they are on track as expected, if not, then appropriate changes can be made – but at least there will be transparency.
Ensure all the key people involved in the knowledge management strategy are present to discuss goals and objectives, they will have valid views – all of which must be considered.
Common knowledge management objectives involve:
- Reducing operational overheads and support costs
- Promoting contact centre efficiency
- Improving CSAT and NPS scores
- Optimising the customer journey online
- Supporting business growth
- Supporting new product/service innovation
Once overall goals have been agreed, bitesize objectives can be decided alongside a timeline.
Knowledge Management Auditing
Once your team has a shared understanding of the purpose and outcomes regarding the knowledge management strategy, it is good practice to conduct a knowledge audit. This involves the evaluation of the current knowledge within your company to highlight any strengths, gaps, existing attitudes, opportunities and roadblocks.
Conduct the audit by considering the following:
- What are your company’s requirements surrounding knowledge?
- What current knowledge assets or resources exist within your company?
- What format do they exist in?
- Are they mainly explicit or tacit types of knowledge?
- What gaps exist within your current knowledge offering?
- How is knowledge currently shared around your company?
- What are the roadblocks that are preventing knowledge sharing?
- Do you have a dedicated and accountable knowledge executive?
- Are there any processes already in place?
- Do you utilise any software that enables sharing?
Once the knowledge audit has been carried out, you will have a clear understanding of where your strengths and areas for improvement are. This helps to influence the way in which you execute knowledge management.
People and Processes
Dedicated Knowledge Executive
Whether its a Knowledge Manager or dedicated executive from a division such as Customer Service, Customer Experience or Marketing, it’s fundamental that you have someone that takes ownership and accountability over knowledge management.
Ensure that your knowledge executive has the skill and experience to deal with knowledge. This includes knowing how to collect, curate, and harvest knowledge, but also involves the translation of tacit data into consumable knowledge.
Without a Knowledge Manager or equivalent in place, your knowledge will become ineffective, inconsistent and redundant. Without a dedicated individual updating, editing and adding to your bank of knowledge then not only does knowledge management not work as a function but inaccurate and therefore potentially damaging information can circulate.
Knowledge Management Process
Process is imperative when it comes executing your knowledge management strategy. Whilst there is no cookie-cutter approach to this and steps will differ from business to business, it’s important to follow the knowledge management process at the least in its’s simplest form:Discovery:The first step concerns identifying and capturing any explicit knowledge that already exists within the company. This can be found in intranets, DMS and shared company documents, for example, HR policies and Sales processes.
Capture: This focuses on extracting any tacit, undocumented knowledge which generally resides within the brains of senior employees. Interviews and reflection exercises are used to harvest knowledge that would otherwise remain subconscious.
Organise: Once all data has been collected, it must be analysed, grouped and translated into digestible content that is familiar with its audiences. This means communicating data as knowledge articles that are written in the company’s tone of voice.
Share: Using knowledge management software such as an intelligent knowledge base, the sharing of knowledge amongst colleagues and with other stakeholders such as customers is seamless and secure. Knowledge bases that utilise AI and Natural Language Processing (NLP) ensure knowledge is fully accessible.
Evaluate: This fundamental step focuses on the constant review and monitoring of knowledge to ensure it is always accurate, up-to-date and serving its audiences effectively. Such evaluation exercises can be carried out using analytics.
This approach can be used time and time again for the effective flow of knowledge to a range of outlets. Ensure each step is given careful attention and that none are skipped or disregarded.
Read more about the Knowledge Management Process stages, here.
Knowledge Management Software
At the heart of your knowledge management strategy is knowledge management software. It is what essentially facilitates the discipline – which would fail without such systems in place.
Most commonly businesses utilise knowledge bases that are powered by AI to act as their centralised repository of companywide knowledge. It stores all knowledge articles surrounding your company, products and services and allows knowledge executives to add, edit and update in real-time to avoid any information inconsistencies.
With a knowledge base, knowledge sharing is simplified. Whether it’s your employees, agents or customers accessing knowledge, the utilisation Natural Language Processing (NLP) ensures that the right information is always delivered.
For instance, agents who are accessing the internal-facing knowledge base begin by typing a customer query into the search bar. NLP gets to work unpicking the query, analysing the keywords, intent, grammar used and popularity, so that no matter how a query is phrased, the best results are produced.
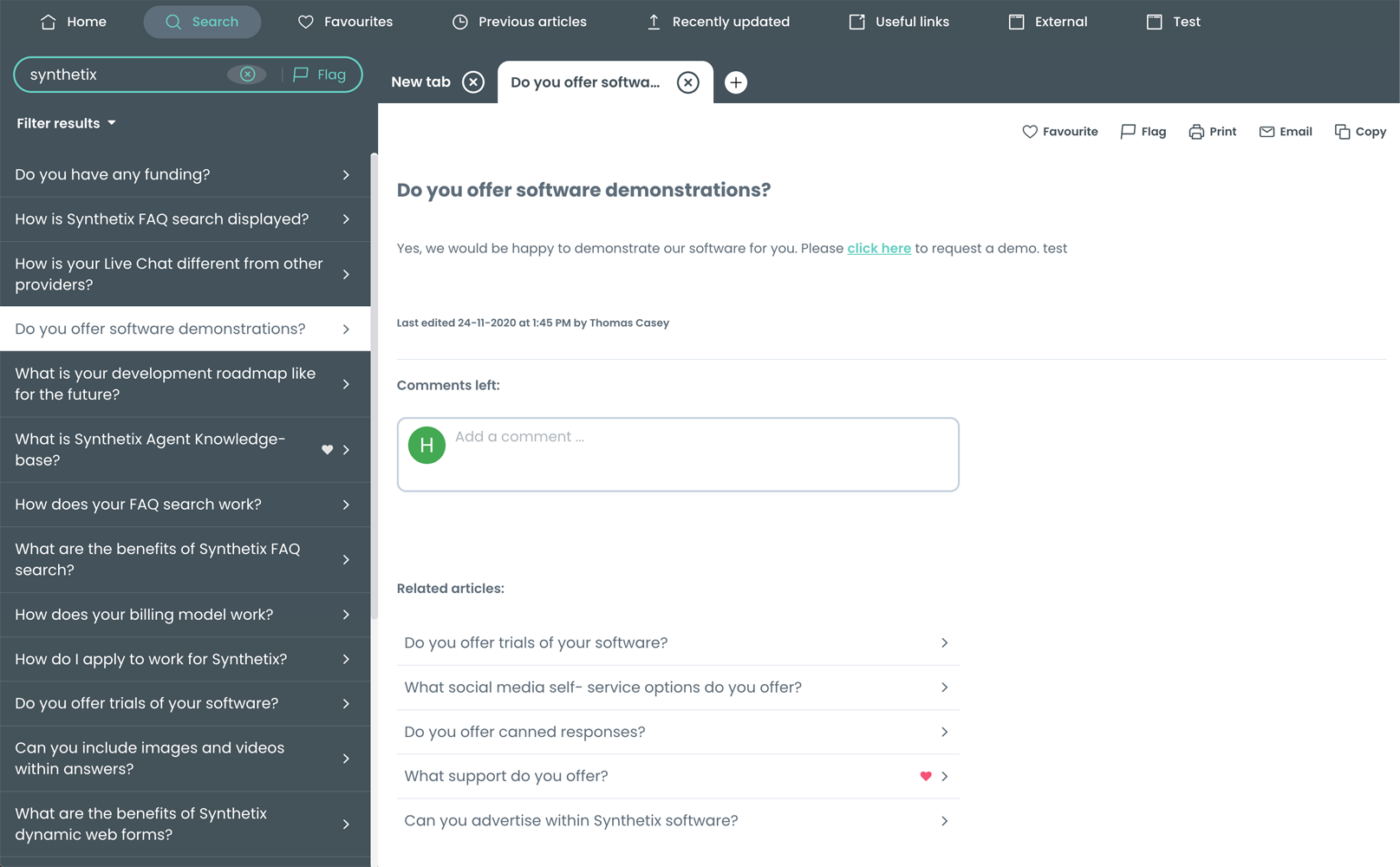
From a customer’s perspective, a filtered version of your knowledge base can be accessed via a number of online self-service tools. When a customer requires support or needs to solve an issue, they can either navigate to a knowledge article by choosing a category or NLP will produce relevant answers based on what is entered.
For effective knowledge management software, consider:
- Is it powered by AI and does it harness NLP?
- Is it built with both contact centres and customers in mind?
- Does it enable seamless integrations with other key systems?
- Is it implemented using low-code?
- Does it use open RESTful open APIs?
Check out the Knowledge Management Software Buyer’s Guide
Implementation
The implementation of knowledge management software – that is from the SRS agreement to being fully up and running – does not need to be complicated or time-consuming. By choosing knowledge management software that utilises low code, depending on your business requirements, your employees and customers could be benefiting from knowledge within days or weeks. All it requires is a simple line of code that is installed on your website.
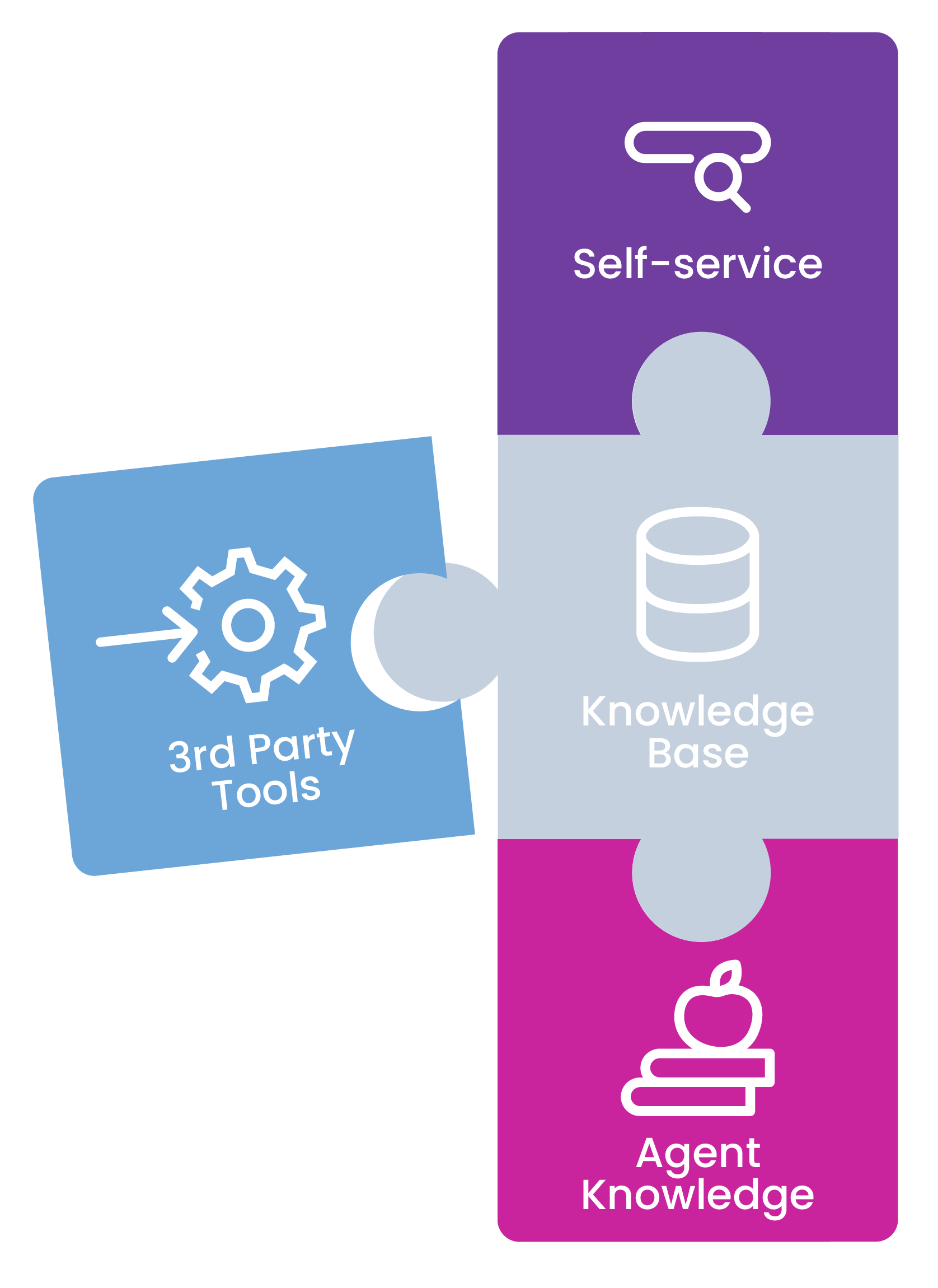
Your knowledge base seamlessly integrates with your fundamental customer service tools for the two-way sharing of knowledge. whether it’s self-service widgets , chatbots or live chat , all users can access consistent information fed from the same source.
Through its open RESTful API capabilities, an intelligent knowledge base can also connect to any key 3rd party applications that your company relies on, for example, your CRM.
Measurement and Maintenance
Your knowledge base’s analytical suite is how you will determine how effective your knowledge management strategy has proved in terms of achieving your overall objectives. Whether your objectives surrounded CSAT or agent efficiency, it is critical to the success of knowledge management that metrics are constantly analysed and reviewed.
Investing significant time and capital into the execution of your knowledge management strategy, only to fail at the final hurdle would be detrimental – and is why measurement is so important.
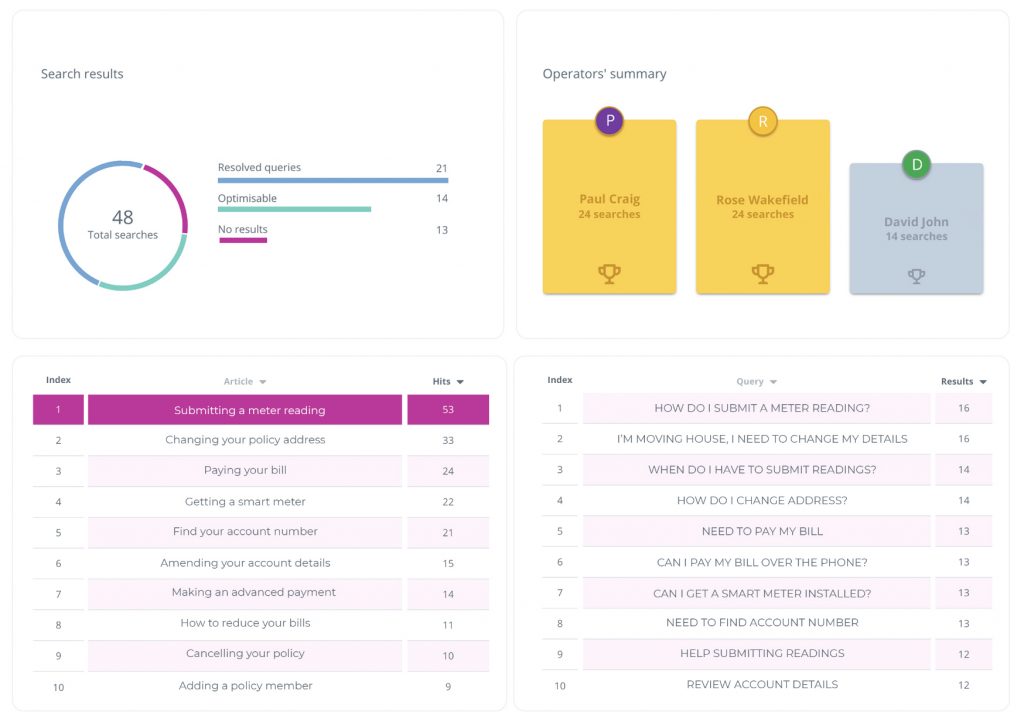
Just some knowledge analytics that are available to companies for analysis include:
- Search results: helping you to determine the effectiveness of knowledge, revealing how many articles resolved queries and how many required further optimisation.
- Top queries: providing an insight into customer behaviour, revealing what is being searched and whether knowledge articles were available to fulfil their requirements.
- Triggers: demonstrating which tools have been triggered on your website and which have proved the most optimal at resolving issues.
If you enjoyed this article and would like to more about knowledge management,t, you can read our guide here, or for advice on knowledge management software and implementation, please


